Lab grown meat, or synthetic alternative protein (SAP), begins with a biopsy on an embryo within a subject animal. First, a long, thin needle is inserted through the skin of a pregnant cow, chicken, or pig. The needle penetrates the embryo within the mother animal’s uterus, a pear-shaped organ, and stem cells or satellite cells are extracted. Typically, SAP is produced from stem cells.
- Stem cells can become any type of cell, including fat, bone, or muscle. They are capable of differentiation, the transition of one cell type to another.
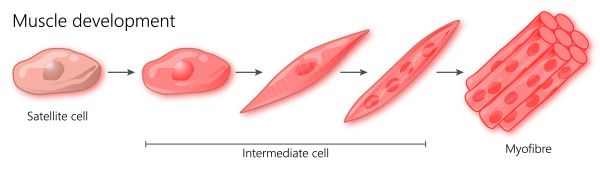
- Satellite cells can only become skeletal muscle cells. In meat, muscle tissue is the main ingredient.
After the embryonic cells are extracted, they are added to a culture medium that promotes cellular growth. This medium is typically a liquid that contains various specialized substances. The following sections examine stem cells, satellite cells, and the culture medium that SAP producers use in greater detail.
Stem Cells
As the Mayo Clinic explains, “Stem cells are the body’s raw materials, cells from which all other cells with specialized functions are generated.” In other words, stem cells can develop into almost any part of the organism from which they are obtained. Examples include skin, bones, organs, connective tissue, and hair. Ultimately, the growth factors that are used in the culture medium determine which type of cells the stem cells become. These growth factors are naturally occurring, biologically active molecules that regulate cell growth, division, and proliferation.
Satellite Cells
Satellite cells can only develop into muscle tissue, which is highly specialized because its cells can shorten or contract. The cellular elements within muscle tissue have an elongated shape and are called muscle fibers, or myofibers. Each myofiber contains multiple myotubes. The reason satellite cells are used in SAP production is that the main component of meat is muscle tissue. In turn, the main ingredient of muscle tissue is water, and the second largest component is protein.

Culture Medium
After the biopsy is performed, technicians working in a cleanroom environment add the extracted cells to a culture medium. This mixture of substances promotes and supports cellular growth. In the case of stem cells, the culture medium also supports differentiation. A culture medium can use different formulas, but SAP producers typically use a mixture of growth factors, amino acids, fatty acids, salts, vitamins, and trace elements. The purity of the culture medium is important because the SAP industry wants to avoid introducing transmissible diseases.
Today, most SAP producers add fetal bovine serum (FBS) to the culture medium. This controversial substance is the subject of our next article.